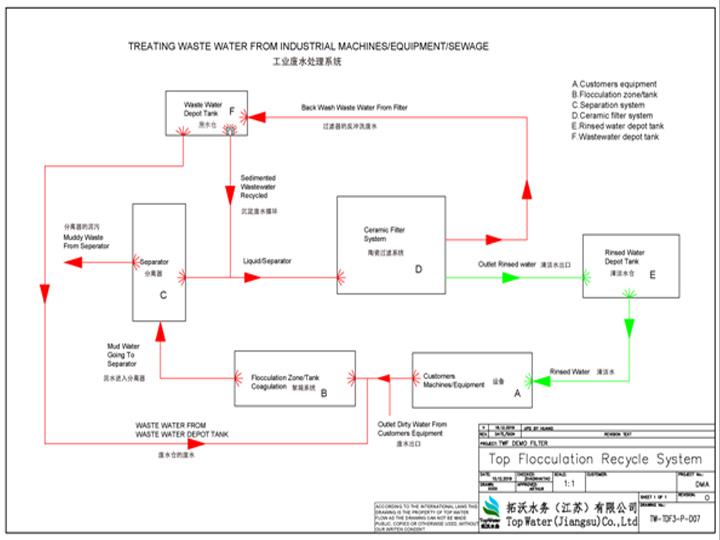
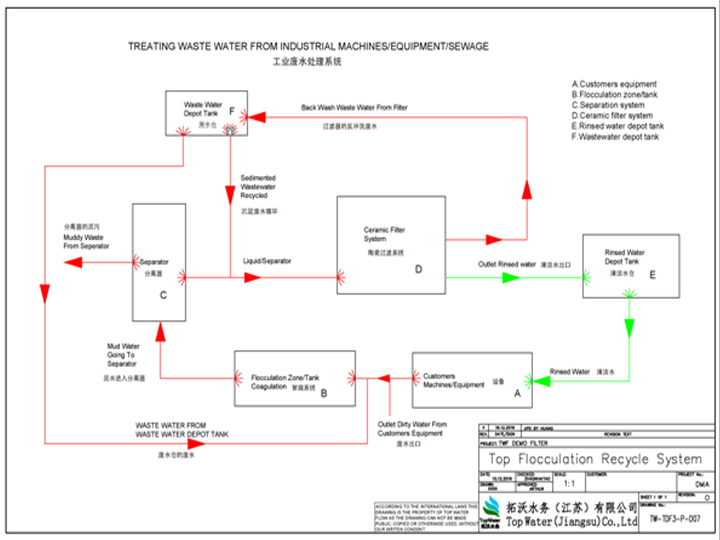
Top Flocculation Recycle System
Description of Top Flocculation Recycle System.
Top Flocculation
recycle system consists of five main parts: a) wastewater flocculation/coagulation
tank;
b) separator and sedimentation tank; c) ceramic filter system; d) rinsed water
depot tank and the
e) wastewater tank and customer’s equipment marked on installation plan as well.
However, based on the guideline of the system, we will also evaluate each
project and provide customized plan according to specific needs.
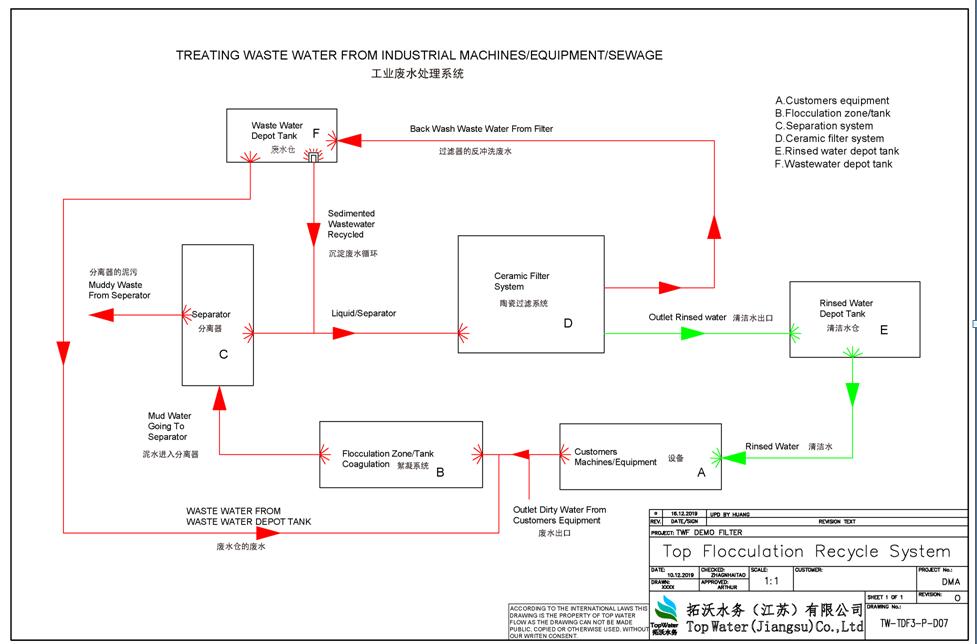
Please see the Top Flocculation Recycle System schema with a basic guideline of installation plan.
Reasons to recycle and reuse process water
· Process water in various industries is mainly installed to clean or mix various medias in various industries.
· It requires special storage for the wastewater and the delivery is often expensive.
· The local government has been more and more strict on wastewater treatment. The law requires the industries to find solutions to recycle the water in the best way.
· Some companies continually rinse the process water, others in shorter intervals, and some reuse the water for 3-5 days before pumping into depot tanks for further treatment.
Problems of reusing
the process water without treatment
· Take the process water from some industry as an example. The wastewater would accumulate many particles, diluted oil and medias, which make it difficult to rinse out by filter.
· Flocculation/coagulation is one step to treat sewage water, by aggregating masses of particles to separate from liquid.
· Reusing process water will cause high maintenance on the equipment because particles and waste will plug and damage the equipment. Flocculation is an easy and quick solution to remove particles in this process.
· Biofilm can cause problems in production line, which ceramic filter system will reduce most of, and it can be supplied with some other technologies to fix the problems if customers have demand on that.
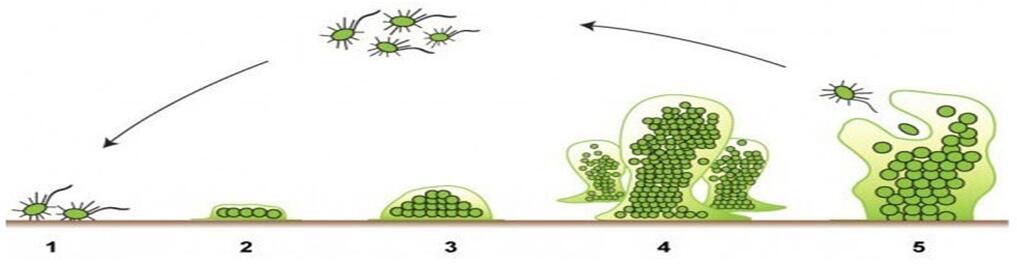
Stages to develop biofilm:
Ø Stage 1. Reversible attachment of the bacterium to the surface. Weak bond between the bacterium and the substrate that happens in barely 1 minute.
Ø Stages 2 y 3. Irreversible attachment to the surface with an initial growth and division phase with the production of a protective exopolymer and the final development of the colony with the dispersion of colonizing cells. The irreversible attachments are formed during a period of between 20 minutes and 4 hours.
Ø Stage 4. Growth and maturation. The resulting bacteria form a micro-colony around the attachment point. If the conditions are appropriate, an organized colony will develop. Along the maturation phase, the biofilm becomes adapted to the presence of nutrients, oxygen and the population changes. It's estimated that the development of this phase takes from 2 to 4 days.
Ø Stage 5. Dissemination of colonizing cells. Finally, some bacteria release themselves from the biofilm matrix so they're able to colonize new surfaces, closing or starting the cycle.
The biofilm formation, attachment, maturation, dissemination and recovery process develops in barely 5 days.
Each part of the system plays the role in the treatment process:
Take the process water from some industry as an example. The wastewater would accumulate many particles and contain oil and medias, which make it difficult to remove by filter. This unique Flocculation recycle system is designed to handle this challenging task.
The process water will get dirty and oily after use, and the treatment often
add solvent into the water. One of the proven technologies to remove this would
be using our flocculation system, build in as a total recycling system.
The guideline of Top Flocculation Recycle System
A) Pumped out of customer’s equipment outlet, the wastewater goes into Unit B flocculation zone/tank
B) Flocculation and coagulation treatment is a simple procedure with complex solvent formula based on the medias been treated.
Most industrial wastewater contains both dissolved and suspended particles. Coagulation and flocculation treatment is used to separate the suspended solid from the water. Suspended particles vary in source, component, size, shape, and also density. Correct application of coagulation and flocculation depends upon these factors.
Coagulation and flocculation treatment reacts in successive steps, allowing particles become viscous and thickened into coherent mass. Followed by sedimentation process (see Sedimentation Chapter), the liquid can be easily separated from floc.
Coagulation
A high-energy, rapid-mix to properly disperse coagulant and promote particle collision are needed to achieve good coagulation. Fully agitating is vital to leave this step completed. The agitating process takes about 1 to 3 minutes.
Flocculation
Flocculation reactor forms submicroscopic microfloc into visible suspended particles. Microfloc particles collide, causing them to bind larger, visible flocs called pinflocs. Floc continues to build with additional collisions and interaction with other polymers.
Macrofloc is formed and high molecular weight polymers, called coagulant aids, which facilitates bridging, binding, and strengthening the floc and shorten settling time. Once floc reaches to optimum size, liquid is ready for sedimentation.
Contact time for flocculation ranges from 15 to an hour or more. Flocculation requires careful attention on the mixing velocity. To prevent floc from tearing apart or shearing, the mixing velocity is usually tapered off as the size of floc grows. Once floc torn apart, it is difficult to get them to reform to their optimum size and strength.
Coagulation Flocculation and Sedimentation
Thedesign incorporates coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation into a single unit (either upflow solid contact unit or sludge blanket unit). Most upflow solid contact unit uses recirculation of previously to enhance floc formation and maximize usage of treatment chemical. Sludge blanket unit forces newly forming flocs to pass upward through a suspended floc.
In both styles of units, the cross-sectional surface of the basin increases from bottom to top, causing water flow to slow as it rises, allowing floc to settle out. The unit generally uses higher rise rate and shorten detention time than conventional treatment. Numerous manufacturers market proprietary units based on this design concept. These unit is compact to install on the location. On-site pilot plant evaluation, by an experienced engineer who has knowledge of the water condition, is recommended in prior to make the plan.
Coagulant Selection
The choice of coagulant chemical is based on the type of suspended solid to be removed, waste water condition, facility design and budget on chemical. Final selection of coagulant should be made with test in consideration of treatment performance, method, dose cost, both sludge handling and disposal cost as well.
Inorganic Coagulant
Inorganic coagulants such as aluminum and iron salts are the most commonly used in the process.
When added to water, these highly charged ions to neutralize the suspended particles. The inorganic hydroxide produces short polymer chains which enhances microfloc formation.
Inorganic coagulant, widely available, usually offers the lowest price per pound. And when properly applied, it is effective on removing most suspended solid. They are also capable of removing a portion of the organic precursors which may combine with chlorine to form disinfection by-product. Inorganic coagulant produces large volume of floc which can also entrap bacteria as they settle.
Inorganic coagulants may alter the pH of the water since they consume alkalinity. When applied in a lime soda ash softening process, alum and iron salts generate demand for lime and soda ash. They also require corrosion-resistant storage and feed equipment. It is important to note that large volume of settled floc must be disposed properly.
C) The floc will be separated from the liquid and medias by Unit C separator.
D) Waste will be pumped out from separator to a waste tank and liquid will be going directly to the Unit D Ceramic filter system.
E) Ceramic filter system will filter down to 0.1 micron in particle size, which will remove the remaining particles and most bacteria in the water.
The ceramic filter system would not remove chemical in the process, which means
the users would save the amount of chemical/detergent in the recycling process
for cleaning parts.
Rinsed water goes into rinsed water depot tanks marked with Unit E and Unit F for further use. The reason of setting up two tanks is that one tank is used to rinse water at all times, so when dirty water goes into dirty water tank, then rinsed water is ready if needed to be reused in the system. When the system treats a small amount of wastewater, it is normally needed one rinsed water depot tank.
The back-wash waste from ceramic filter will be sent to wastewater depot tank (Unit F).
F) Rinsed water tank will be set up, but some industries run this clean water directly in to the process again.
G) Wastewater depot tank will collect waste from the backwash from the ceramic filter system. When the tank is filled up, the wastewater will rinse through the ceramic filter system again to reduce the water and get more concentrated waste before it is drained out.
Top Water Jiangsu suggests that all industrial water related operating systems should be inspected and evaluated, in matter of which treatment is best for the industrial operations and public health. Top Water Jiangsu is willing to inspect the existed water system, make the right treatment plan with the cost of equipment/service and further investment return on our equipment.
Top Water Jiangsu has some recycling basics:
“Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Return on Investment”.
- 2019-10-11 Removal effect and cause analysis of micro-polluted… >
- 2019-09-30 Sewage treatment equipment maintenance and precauti… >
- 2019-08-21 Conditions that must be known about the choice of s… >
- 2019-08-14 Chinese medicine extraction wastewater treatment - … >